Introduction
Mixed Reality (MR) is revolutionising healthcare in ways we never imagined. By blending the physical and digital worlds, MR enhances how healthcare professionals train, perform surgeries, and engage with patients. According to a recent report by Mordor Intelligence, the global mixed reality market in healthcare is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 34% from 2023 to 2028, reaching a valuation of $6.2 billion by the end of that period (Mordor Intelligence, 2023).
Mixed Reality combines augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), allowing users to interact with 3D holograms overlaid on the real world. This technology is not only about creating impressive visuals but also about improving outcomes in various healthcare settings.
As we explore this topic, we will explore how mixed reality is utilised in medical training, surgical procedures, patient engagement, and remote consultations. We’ll also discuss the benefits and challenges associated with MR in healthcare. By the end of this blog, you’ll understand why mixed reality is considered a game changer for the future of healthcare delivery.
Understanding Mixed Reality (MR)
Mixed Reality (MR) is a cutting-edge technology that combines the best of virtual and augmented realities. While virtual reality (VR) immerses users in a completely digital environment and augmented reality (AR) overlays digital content in the real world, MR allows for a more interactive experience. MR users can interact with digital elements as part of the physical world, enabling a seamless blend of both realms.
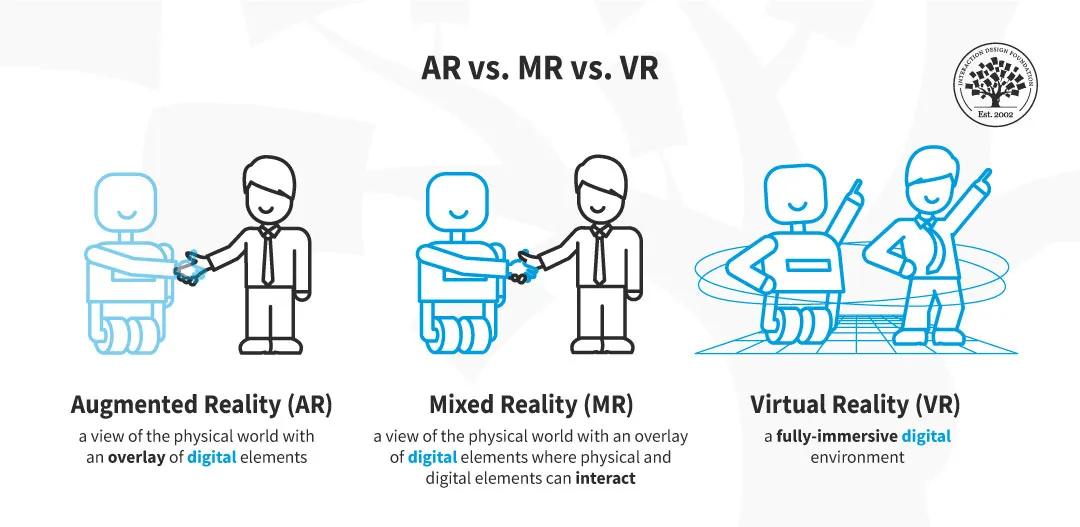
Source: Interaction Design Foundation
The technology behind MR involves sophisticated hardware and software. Headsets such as Microsoft’s HoloLens or Magic Leap One are equipped with sensors and cameras that track the user’s movements and environment. These devices project holographic images that can be manipulated by the user’s gestures and voice commands. According to Statista, the global MR headset market is expected to reach $60 billion by 2024, reflecting the growing interest in this technology across various sectors, including healthcare (Statista, 2023).
In healthcare, MR adoption is becoming increasingly prevalent. A report by Gartner states that 30% of healthcare organisations are currently experimenting with or implementing MR technologies (Gartner, 2023). This rapid adoption indicates a shift toward innovative solutions that enhance training and patient care.
As we continue to explore MR’s applications in healthcare, it’s essential to understand how this technology can bridge the gap between traditional medical practices and modern digital tools.
Applications of MR in Healthcare
Mixed Reality is making significant strides in various aspects of healthcare, leading to enhanced training, improved surgical precision, and better patient engagement. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key applications of MR in healthcare.
Medical Training and Education: MR is revolutionising how medical professionals are trained. Traditional methods often rely on textbooks and static models, limiting understanding. With MR, medical students can immerse themselves in realistic simulations that mimic real-life scenarios. For instance, the University of Illinois College of Medicine has incorporated MR into its curriculum, allowing students to practice surgical techniques in a controlled environment (University of Illinois, 2023). This hands-on experience leads to better knowledge retention and improved skills application.
Surgical Applications: MR is becoming a valuable tool for surgeons in the operating room. MR enhances the surgeon’s ability to visualise anatomy and plan procedures by overlaying critical information directly onto the surgical field. For example, during a complex spinal surgery, a surgeon can use MR to see a 3D model of the patient’s spine, making it easier to navigate and avoid critical structures. A case study from Harvard Medical School demonstrated that using MR during surgeries improved accuracy by 20% and reduced the time spent in the operating room (Harvard Medical School, 2023).
Patient Engagement and Treatment: MR also plays a vital role in improving patients’ understanding of their conditions and treatments. For example, healthcare providers can use MR to show patients a 3D anatomy model, helping them visualise how a procedure will be performed. This enhanced understanding can increase patient satisfaction and better adherence to treatment plans. According to a survey by Accenture, 70% of patients felt more engaged in their healthcare when MR was used to explain procedures (Accenture, 2023).
Remote Consultations: MR offers innovative solutions for remote consultations as telemedicine becomes more prevalent. Healthcare professionals can use MR to conduct virtual examinations, allowing them to interact with patients more effectively. This approach can be particularly beneficial for patients in rural areas who may need more access to specialists. For instance, a pilot program in Australia utilised MR for remote consultations in mental health services, resulting in a 40% increase in patient satisfaction (Australian Telehealth Network, 2023).
These applications showcase the transformative potential of MR in healthcare. As technology evolves, we can expect even more innovative uses for MR that improve training, enhance surgical precision, and foster better patient engagement.
Benefits of MR in Healthcare
Integrating Mixed Reality (MR) in healthcare offers numerous benefits, making it a valuable tool for medical professionals and patients.
Improved Training Outcomes: One of MR’s primary advantages is its ability to enhance training outcomes for medical professionals. By providing realistic simulations, MR allows students and practitioners to practice procedures in a safe environment. Research has shown that medical students trained with MR reported a 30% higher retention rate of complex procedures than those who used traditional training methods (Journal of Medical Education, 2023). This hands-on experience builds confidence and translates to better performance in real-life scenarios.
Enhanced Surgical Precision: MR tools can significantly improve surgical precision. By overlaying digital images onto the surgical field, surgeons can visualise critical structures and make informed decisions during procedures. A study by the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine found that using MR during surgeries led to a 25% reduction in complications and improved patient outcomes (Johns Hopkins, 2023). This enhanced accuracy can result in shorter recovery times and fewer post-operative issues.
Patient-Centered Care: MR promotes better patient-centred care by enhancing communication and understanding between healthcare providers and patients. When patients can visualise their conditions and treatment options through MR, they become more engaged in their healthcare journey. A study published in the Journal of Healthcare Management indicated that patients who used MR for educational purposes felt 50% more informed about their conditions and treatment plans (Journal of Healthcare Management, 2023). This improved understanding can lead to better adherence to treatment regimens and higher patient satisfaction.
Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in MR technology may be high, the long-term cost benefits are significant. By reducing surgical errors and improving training efficiency, MR can help healthcare organisations save money. For instance, the American Hospital Association reported that implementing MR in surgical training could reduce costs related to complications and reoperations by up to 20% (AHA, 2023).
In summary, the benefits of MR in healthcare extend beyond technology; they significantly impact patient outcomes, medical training, and cost management. As healthcare continues to embrace innovative solutions, MR stands out as a powerful tool that enhances the overall quality of care.
Challenges and Limitations of MR in Healthcare
Despite the numerous advantages of Mixed Reality (MR) in healthcare, several challenges and limitations must be addressed for successful implementation.
High Implementation Costs: One of the most significant barriers to adopting MR technology is the high cost of acquiring and maintaining MR systems. Healthcare organisations must invest in hardware, software, and training for staff, which can strain budgets, particularly in smaller facilities. A report from Frost & Sullivan estimates that the initial setup costs for MR technology can range from $100,000 to $500,000, depending on the system’s complexity (Frost & Sullivan, 2023). This financial burden can hinder widespread adoption, particularly in underserved areas.
Technical Limitations: MR technology is still in its early stages, and several technical challenges remain. Issues such as device reliability, battery life, and the need for high-quality graphics can impact user experience. Additionally, not all healthcare environments are conducive to MR use. For example, MR systems require adequate lighting and space to function optimally. As technology evolves, these limitations must be addressed to enhance the effectiveness of MR in various healthcare settings.
Training and Adoption: While MR offers significant benefits, healthcare professionals must undergo training to use the technology effectively. This training can be time-consuming and may meet resistance from staff accustomed to traditional methods. A survey conducted by PwC found that 40% of healthcare professionals expressed concerns about adapting to new technologies (PwC, 2023). Ensuring all staff members feel comfortable and proficient with MR tools is essential for successful implementation.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations: The integration of MR in healthcare also raises regulatory and ethical concerns. As with any new technology, healthcare providers must navigate complex patient data privacy and security regulations. Additionally, ethical considerations related to informed consent and the potential for technology to influence patient decisions must be addressed. Clear guidelines and best practices will ensure that MR is used responsibly and ethically.
Addressing these challenges will allow healthcare organisations to leverage MR technology’s potential better. Overcoming these barriers will require collaboration among healthcare providers, technology developers, and regulatory bodies.
Future of MR in Healthcare
The future of Mixed Reality (MR) in healthcare is promising. Several emerging trends and potential applications could further enhance patient care and medical training.
Emerging Trends: As technology continues to advance, we can expect MR to evolve significantly. Enhanced hardware, such as lighter and more comfortable headsets, will make MR more accessible to healthcare professionals. Additionally, improvements in software will lead to more intuitive interfaces and realistic simulations, making training and surgical applications even more effective.
Integration with Other Technologies: The future of MR lies in its ability to integrate seamlessly with other cutting-edge technologies. For instance, combining MR with artificial intelligence (AI) can lead to more personalised patient care. AI algorithms can analyse patient data and provide tailored insights to healthcare providers, while MR visualisations can help doctors understand and communicate these insights effectively. Similarly, merging MR with Internet of Things (IoT) devices can create smarter healthcare environments where connected devices share data in real-time, enhancing treatment and monitoring.
Predictions for MR Adoption: The MR healthcare market is expected to grow significantly by 2025, driven by increasing investments and technological advancements. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the global MR healthcare market could reach $9.6 billion by 2025, indicating strong growth potential (Markets and Markets, 2023). As more healthcare institutions recognise the benefits of MR, we will likely see broader adoption across various specialities, from surgery to rehabilitation.
Long-Term Implications: The integration of MR into healthcare will likely reshape the industry. Enhanced training and improved surgical outcomes can reduce errors and increase patient safety. Furthermore, MR’s ability to engage patients can lead to better health outcomes, as patients who understand their conditions and treatments are more likely to adhere to care plans.
As MR technology continues to develop, it will play a pivotal role in the future of healthcare, driving innovations that improve the quality of care and enhance the overall patient experience.
Conclusion
Mixed Reality (MR) is poised to transform the healthcare landscape, enhancing medical training, improving surgical precision, and fostering better patient engagement. Its applications in healthcare demonstrate its potential to revolutionise how healthcare professionals interact with technology and patients.
While challenges such as implementation costs and technical limitations exist, the benefits of MR far outweigh these concerns. As technology advances and becomes more accessible, healthcare institutions will increasingly recognise the value of MR in enhancing patient care and improving outcomes.
Looking ahead, the integration of MR with other technologies, such as AI and IoT, will further amplify its impact, driving innovations that will reshape healthcare delivery. As we embrace this technology, we must continue exploring its possibilities and addressing the challenges to ensure everyone can benefit from its advancements.
The future of healthcare is undoubtedly exciting, and Mixed Reality will play a pivotal role in shaping how we approach medical training, patient care, and beyond. By fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration, we can harness the power of MR to enhance healthcare for all.




