Introduction
5G networks are set to revolutionise how we connect and transfer data. By offering faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity, 5G is transforming industries and enhancing our daily lives. A staggering statistic from GSMA Intelligence predicts that by 2025, there will be 1.7 billion 5G connections worldwide, highlighting the widespread adoption of this technology (GSMA Intelligence, 2023).
5G, or fifth-generation wireless technology, represents a significant leap from its predecessor, 4G. While 4G brought us faster mobile internet and streaming capabilities, 5G takes it further by enabling near-instantaneous data transfer and supporting a vast array of connected devices.
This blog will explore how 5G networks reshape connectivity and data transfer across various sectors. We’ll delve into the evolution of mobile networks, the key features of 5G, its applications in different industries, the economic impact, and the challenges and concerns surrounding its implementation. By understanding these elements, we can appreciate how 5G will play a pivotal role in the future of communication and technology.
The Evolution of Mobile Networks
Mobile networks have advanced significantly since the introduction of the first-generation (1G) technology. Each new generation has brought significant advancements, paving the way for today’s interconnected world.
1G was primarily focused on voice services, allowing users to make calls on the go. However, it had limitations like poor sound quality and a lack of data services. The introduction of 2G brought SMS (text messaging) and basic data services, enabling more efficient communication.
The leap to 3G revolutionised mobile internet access, allowing for multimedia support and faster data speeds. Users could now browse the web and stream music and videos, marking a significant step forward in mobile technology. By the time 4G rolled out, the focus shifted to enhanced mobile broadband, enabling high-definition video streaming, online gaming, and seamless social media usage. According to Cisco, global mobile data traffic increased 74% in 2022, largely driven by 4G networks (Cisco, 2023).
The transition to 5G is a game changer. Unlike its predecessors, 5G is designed to support many devices simultaneously, making it a crucial Internet of Things (IoT) component. It offers up to 10 Gbps, approximately 100 times faster than 4G. This advancement is essential as more devices connect to the internet, from smart appliances to autonomous vehicles.
5G is not just about speed; it’s also about enabling new technologies and previously impossible applications. Its low latency—around one millisecond compared to 30-50 milliseconds for 4G—5G opens up opportunities for real-time applications, such as remote surgery and augmented reality gaming. As we explore the key features of 5G, it’s clear that this technology is set to revolutionise how we connect and interact with the world around us.
Key Features of 5G Networks
5G networks come packed with impressive features that set them apart from previous generations. These advancements are crucial for enhancing connectivity and data transfer capabilities across various sectors.
High Speed: One of the most talked-about features of 5G is its speed. With the potential to reach up to 10 Gbps speeds, 5G can download a full-length HD movie in seconds. This speed is not just about convenience; it enables new possibilities in content consumption, such as streaming 8K videos and supporting virtual reality experiences. A study by Nokia found that 5G could facilitate data-intensive applications that 4G simply cannot support (Nokia, 2023).
Low Latency refers to the delay before a data transfer begins following an instruction. 5G technology significantly reduces latency to around one millisecond. This near-instantaneous response time is crucial for applications that require real-time interactions, such as online gaming, autonomous vehicles, and remote surgeries. Imagine a surgeon operating on a patient miles away; with 5G, the delay between their commands and the surgical robot’s movements is virtually eliminated.
Increased Capacity: 5G networks can support up to 1 million devices per square kilometre. This is vital as the number of connected devices continues to grow. In a world increasingly reliant on IoT, where everything from home appliances to industrial machinery connects to the internet, 5G ensures that networks can handle the influx of devices without compromising performance.
Enhanced Reliability: 5G networks are designed to provide a more reliable connection, even in crowded areas where many devices are connected simultaneously. This reliability is essential for critical applications such as emergency services and public safety communications. A Qualcomm report highlighted that 5G networks will enable better coverage in rural areas and improved connectivity in urban environments (Qualcomm, 2023).
In addition to these key features, 5G supports advanced technologies like network slicing, allowing operators to create multiple virtual networks within a single physical network. This capability ensures that specific applications receive the bandwidth and latency required, further optimising network performance.
The remarkable features of 5G networks position them as a transformative force in connectivity and data transfer. As we explore the various applications of 5G technology, it becomes clear how these features will change the landscape of communication and innovation across different industries.
Applications of 5G Technology
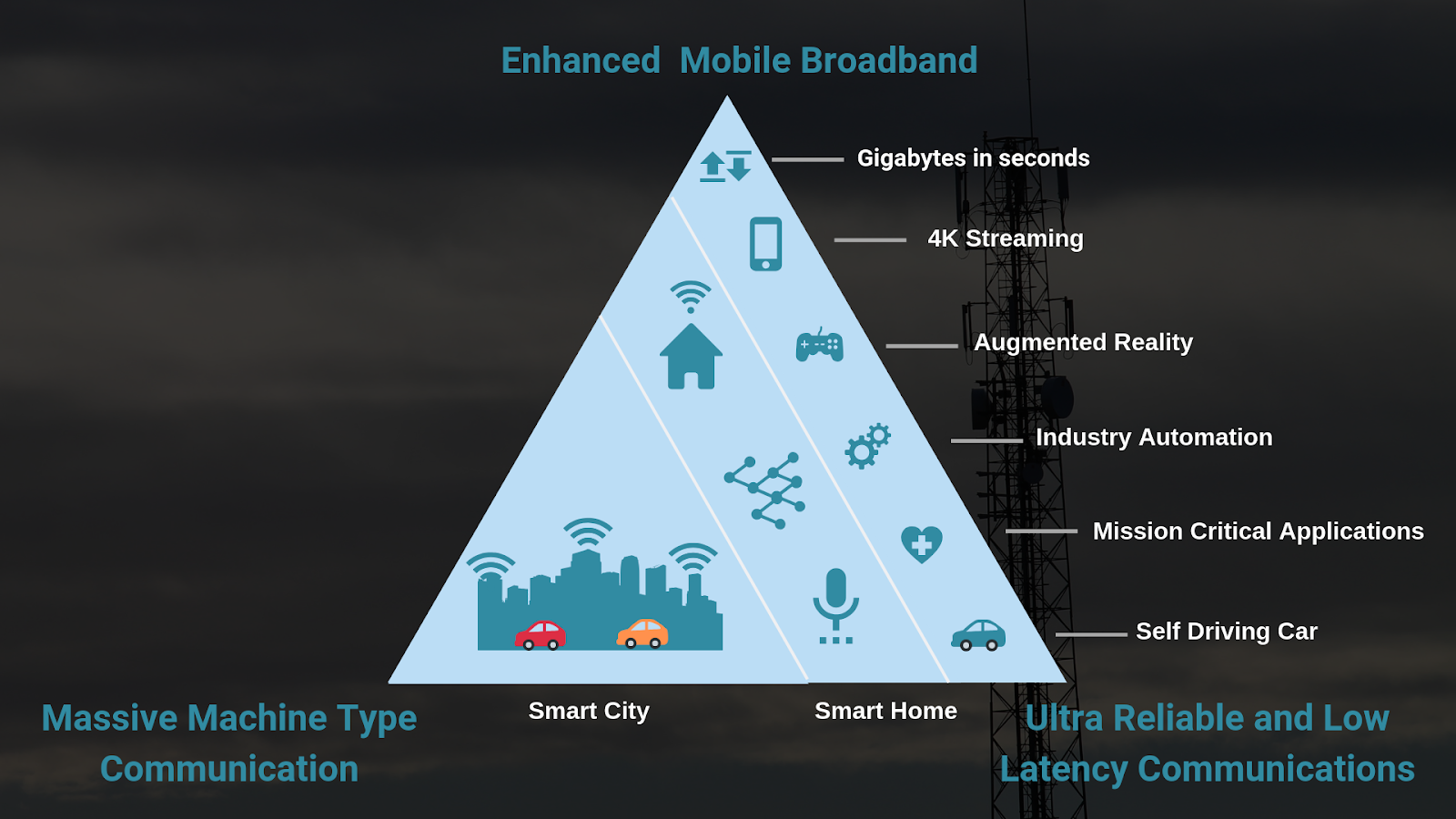
Source: GreyB
5G technology has the potential to revolutionise numerous industries, enhancing services and enabling previously unimaginable innovations. Here are some key applications of 5G technology:
Healthcare: 5G is set to transform the healthcare industry through telemedicine and remote patient monitoring. With its low latency and high-speed data transfer, doctors can perform remote surgeries using robotic systems. For instance, a hospital in Germany successfully conducted a remote surgery over a 5G network, demonstrating its potential to save lives, particularly in emergencies. Additionally, wearable devices can continuously monitor patients’ vital signs and transmit data to healthcare providers in real-time, leading to quicker diagnoses and treatments.
Smart Cities: The concept of smart cities relies heavily on 5G technology. With increased capacity and reliability, cities can integrate smart traffic systems, energy management, and public safety measures. For example, 5G can enable real-time monitoring of traffic conditions, allowing for smarter traffic signals that reduce congestion and improve air quality. Additionally, smart streetlights with sensors can adjust brightness based on pedestrian activity, saving energy and enhancing safety.
Automotive Industry: Connected vehicles are another area where 5G technology shines. The automotive industry is rapidly advancing towards fully autonomous vehicles that rely on real-time data exchange between vehicles and infrastructure. 5G can facilitate vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, enabling cars to communicate with each other and surrounding infrastructure to avoid accidents and optimise routes. A report from McKinsey suggests that by 2030, the connected vehicle market could be worth $1.5 trillion, largely driven by 5G advancements (McKinsey, 2023).
Entertainment and Media: The entertainment industry is set to benefit significantly from 5G technology. Streaming services, such as 8K video, with high-speed data transfer, can offer higher-resolution content. Moreover, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications will become more mainstream, providing immersive experiences for users. For instance, the NBA has partnered with telecommunications companies to deliver 5G-powered AR experiences during live games, enhancing fan engagement.
Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: 5G technology will also play a crucial role in the next industrial revolution, often called Industry 4.0. Factories with 5G networks can implement smart manufacturing processes that rely on real-time data analysis and automation. For example, connected machines can communicate with each other to optimise production schedules and reduce downtime. According to Ernst & Young, 5G could help manufacturers save up to 30% in operational costs through increased efficiency and productivity (Ernst & Young, 2023).
These applications highlight just a few ways that 5G technology is set to reshape various sectors, improving connectivity and enhancing data transfer capabilities. As we delve into the economic impact of 5G, we can better understand its broader implications.
The Economic Impact of 5G
The economic implications of 5G technology are vast, promising significant benefits for businesses and economies worldwide.
Job Creation: The rollout of 5G networks is expected to create millions of jobs in various sectors, from telecommunications to manufacturing. A report from IHS Markit estimates that 5G could generate 22 million jobs globally by 2035 as companies invest in infrastructure and develop new applications (IHS Markit, 2023). These jobs will range from network engineers to data analysts, reflecting the broad impact of 5G on the job market.
Boosting Innovation: 5G fosters industry innovation by enabling new technologies and applications. Startups and established companies are leveraging 5G capabilities to develop innovative solutions. For example, companies in the tech and automotive sectors are creating applications for autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and enhanced telemedicine services. This wave of innovation can lead to increased competition and drive economic growth.
Impact on GDP: Introducing 5G networks will contribute significantly to global GDP growth. According to a study by Ericsson, 5G could add $6.3 trillion to the global economy by 2030 (Ericsson, 2023). This growth will come from improved productivity, enhanced consumer experiences, and emerging new markets driven by 5G technology.
Furthermore, 5 G’s capabilities will increase efficiency and cost savings in healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. For instance, remote monitoring in healthcare can reduce hospital visits, lowering costs for both providers and patients.
Governments also recognise 5 G’s economic potential and invest in infrastructure to facilitate its rollout. Policies that support the deployment of 5G networks can improve connectivity and spur economic development in underserved areas.
In summary, the economic impact of 5G technology is significant, with job creation, innovation, and GDP growth at the forefront. As businesses and governments embrace this technology, the potential benefits will continue to unfold, driving progress in various sectors.
Challenges and Concerns Surrounding 5G Implementation
While 5G technology promises numerous benefits, several challenges and concerns accompany its implementation. Addressing these issues is crucial for ensuring a successful rollout.
Infrastructure Requirements: Deploying 5G networks requires significant infrastructure upgrades. Unlike previous generations, 5G relies on a denser network of small cells to provide coverage, particularly in urban areas. Telecommunications companies must invest heavily in building new towers and upgrading existing infrastructure. A report from Deloitte estimates that the U.S. will need to invest $130 billion in infrastructure over the next decade to deploy 5G (Deloitte, 2023) fully.
Security Concerns: The increase in connectivity that comes with 5G also raises security concerns. As more devices connect to the internet, the potential for cyberattacks grows. Hackers may exploit vulnerabilities in connected devices or the network itself. The Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has warned about the potential risks associated with 5G, urging organisations to implement robust security measures to protect their networks (CISA, 2023).
Health Concerns: Public concerns about the health effects of 5G radiation have also emerged. While scientific consensus indicates that 5G technology operates within safe exposure limits, some individuals remain sceptical. Studies on the long-term health effects of 5G are ongoing, and public apprehension may affect its adoption. Effective communication and education about the safety of 5G technology will be essential in addressing these concerns.
Regulatory Challenges: Governments must navigate regulatory frameworks to facilitate 5G deployment. Issues such as spectrum allocation, zoning laws, and environmental regulations can slow the rollout process. Collaboration between government agencies, telecommunications companies, and local communities will be essential to streamline the regulatory process and ensure timely implementation.
Digital Divide: Finally, the rollout of 5G technology risks exacerbating the digital divide. While urban areas may benefit from enhanced connectivity, rural and underserved communities may be left behind if infrastructure investments do not reach these regions. Policymakers must prioritise equitable access to 5G technology to ensure all communities benefit from its advantages.
Addressing these challenges and concerns will be vital as we move toward widespread adoption of 5G networks.
The Future of 5G and Beyond
The future of 5G technology holds exciting possibilities but poses new challenges and considerations.
6G and Emerging Technologies: While 5G is still being rolled out, research into 6G is already underway. Expected to launch around 2030, 6G promises even greater speeds—potentially exceeding 100 Gbps—and advanced capabilities such as holographic communication and enhanced AI integration. The focus will likely shift towards integrating technologies like terahertz waves, which could provide unprecedented bandwidth and connectivity options.
Global Adoption Trends: As of 2023, 5G adoption is rising globally. According to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), there are over 1 billion 5G subscriptions worldwide, with significant growth expected in the coming years (ITU, 2023). Countries such as South Korea, China, and the United States are leading the charge in 5G deployment while developing nations are working to improve their infrastructure to catch up.
Long-Term Implications: The widespread adoption of 5G will have profound long-term implications for connectivity and data transfer. As businesses and consumers embrace 5G technology, we can expect an increase in IoT devices, smart cities, and autonomous vehicles. This shift will reshape industries and drive economic growth.
Moreover, the continuous evolution of connectivity will redefine how we interact with technology. For example, integrating augmented and virtual reality in everyday applications will enhance user experiences in gaming, education, and training.
However, as we look toward the future, addressing the challenges mentioned earlier will be essential, including infrastructure investment, security, and equitable access. The success of 5G and future technologies depends on collaboration among governments, industries, and communities to build a connected world that benefits everyone.
Conclusion
The arrival of 5G networks marks a significant milestone in connectivity and data transfer evolution. With unprecedented speeds, low latency, and increased capacity, 5G technology is revolutionising various sectors, from healthcare to entertainment. Its immense potential to enhance applications and foster innovation drives economic growth and job creation.
As we explore the numerous applications of 5G, it becomes clear that this technology will fundamentally reshape our interactions with the world around us. However, the rollout of 5G also presents challenges, including infrastructure requirements, security concerns, and the risk of exacerbating the digital divide. Addressing these challenges will be crucial to successfully implementing 5G technology.
Looking ahead, the future of 5G and beyond holds exciting possibilities. With the emergence of 6G and the continued integration of advanced technologies, we are on the brink of a new era of connectivity that will transform how we live and work. As we embrace these advancements, we must remain informed and engaged in the conversation about the implications of 5G technology.
The journey towards a more connected world has just begun, and 5G networks are leading the charge toward a brighter, more innovative future.




